Assessing the Cooling Effects of Urban Parks and Their Potential Influencing Factors: Perspectives on Maximum Impact and Accumulation Effects
发表期刊:Sustainability
分区:SCI三区
影响因子:3.3
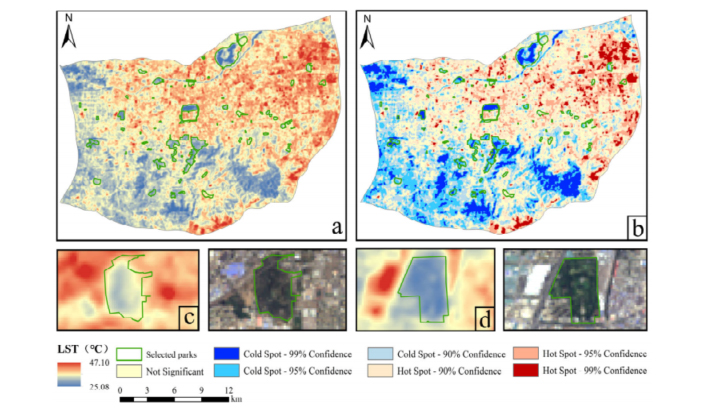
Urban parks play an essential role in mitigating the urban heat island (UHI) effect driven by urbanization. A rigorous understanding of the cooling effects of urban parks can support urban planning efforts aimed at mitigating the UHI effect and enhancing urban sustainability. However, previous research has primarily focused on the maximum cooling impact, often overlooking the accumulative effects arising from spatial continuity. The present study fills this gap by investigating 74 urban parks located in the central area of Jinan and constructing a comprehensive cooling evaluation framework through two dimensions: maximum impact (Park Cooling Area, PCA; Park Cooling Efficiency, PCE) and cumulative impact (Park Cooling Intensity, PCI; Park Cooling Gradient, PCG). We further systematically examined the influence of park attributes and the surrounding urban structures on these metrics. The findings indicate that urban parks, as a whole, significantly contribute to lowering the ambient temperatures in their vicinity: 62.3% are located in surface temperature cold spots, reducing ambient temperatures by up to 7.77 °C. However, cooling intensity, range, and efficiency vary significantly across parks, with an average PCI of 0.0280, PCG of 0.99 °C, PCA of 46.00 ha, and PCE of 5.34. For maximum impact, PCA is jointly determined by park area, boundary length, and shape complexity, while smaller parks generally exhibit higher PCE-reflecting diminished cooling efficiency at excessive scales. For cumulative impact, building density and spatial enclosure degree surrounding parks critically regulate PCI and PCG by influencing cool-air aggregation and diffusion. Based on these findings, this study classified urban parks according to their cooling characteristics, clarified the functional differences among different park types, and proposed targeted recommendations.